The Jigsaw ransomware strain first appeared in early 2016. Since then, several variants of the strain have also cropped up. Also known as the BitcoinBlackmailer, it targets systems using Windows operating system.
The basic premise remains the same as any other ransomware attack, i.e., the victim's data is encrypted and held hostage until the ransom amount is paid. But here's how it gets more sinister: While most ransomware attacks threaten to delete user data or deny access unless the ransom is paid, Jigsaw ransomware actually follows through if the ransom is not paid within the specified time.
It is believed to be inspired by the popular horror movie franchise, Saw; John Kramer, aka, the Jigsaw Killer, was the main antagonist of this movie franchise. Jigsaw ransomware even uses the image of Billy, the puppet from the movie, in the ransom note. In the movie series, the puppet was used by the Jigsaw Killer to communicate with his test subjects by delivering recorded messages.
This is definitely not the first time that a ransomware strain has threatened to delete files; however, this is the first one to actually carry out that threat. And what makes it worse is how it deletes files, with more files getting deleted the longer it takes the user to pay the ransom.
Once infected, a threatening notice is displayed on the victim's desktop along with a countdown timer, deleting user files by the hour if the ransom is not paid. It starts by deleting one file every hour, but as the timer reaches closer to 72 hours, more files are deleted each hour. After the first 24 hours, hundreds of files are deleted; by 48 hours, thousands of files per hour are deleted, and finally, if the ransom is still not paid by 72 hours, all remaining files are deleted.
And that’s not all. If the victim attempts to reboot the system, the ransomware restarts and deletes 1,000 files from their system as punishment. There were rumors that the ransom note also stated that if the victim tried to terminate the ransomware process, another 1,000 files would be deleted. This part was, however, later found to be untrue.
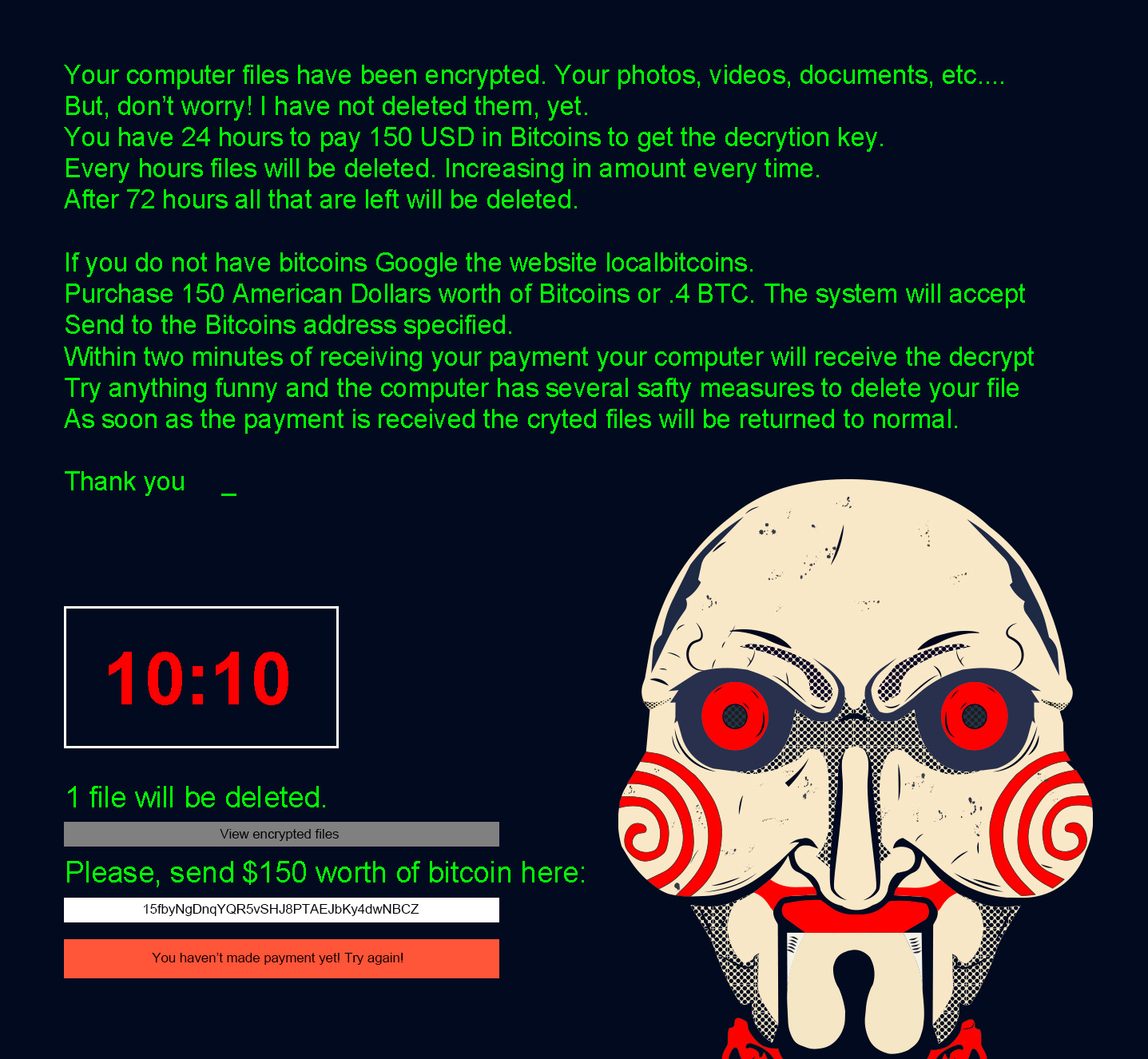
A typical desktop screen of a Jigsaw ransomware infected computer
The malware variant is written in .NET and uses the AES encryption algorithm to encrypt files. Jigsaw can target and encrypt over 200 different file types including, JPEG, RAW, TIF, GIF, PNG, BMP, WMA, DOC, and DOCX. After encrypting the files, it appends different extensions to them, like FUN, BTC, YOLO, and GWS.
Like most ransomware, Jigsaw typically gets into the system through spam emails. It disguises itself using the names firefox.exe or drpbx.exe. The malicious code is located in %UserProfile%\AppData\Roaming\Frfx\firefox.exe, and it also configures an auto-run process for itself in the startup list, thereby ensuring that it gets restarted every time the system is rebooted. Probably the only silver lining in all this is the fact that Jigsaw doesn’t seem to move laterally in a network; it pretty much encrypts files only on the device in which it was downloaded.
Since its first appearance in 2016, many new variants have come up, each with some variations here and there. While the initial ransom amounts were around $150, later versions have been known to demand more, ranging around $5,000.
Several decryption tools are available these days to retrieve files. Since the threat is time bound, it is crucial to act fast. Before running the decryption tools, users first need to terminate the two Jigsaw processes (firefox.exe and drpbx.exe) in the Task Manager and then disable the startup entries for Firefox and Dropbox in the Startup tab. Based on the variant on a system, it could use either or both of these; so it is crucial to ensure that neither are running.
Once this is done, users can safely run the decryption tools to retrieve their files. While it is relatively easy to decrypt the files once Jigsaw's processes are terminated and the startup entries are removed, this malware variant is still dangerous, since Jigsaw may have already potentially deleted user files, or parts of them, before it was stopped. This is why, once infected, it is critical to act fast and remove the malware.
Analysis of the different variants of this ransomware has led security researchers to believe that the Jigsaw ransomware might not be too complex. In fact, many experts consider it to be quite amateurish given that it can be defeated fairly easily. Jigsaw also hasn’t been all that active since 2021. However, ransomware groups are known to rise from the dead and reemerge with improved, more destructive codes. Therefore it’s crucial that organizations keep themselves protected against such attacks.
An effective security solution that detects threats quickly, investigates the root cause, and takes remedial action is required to protect against the damage caused by ransomware such as JigSaw. Our SIEM solution, ManageEngine Log360, helps prevent attacks by detecting and alerting about any unusual events or activities, and initiating automatic remediation processes. To see how Log360 can help your organization defend against JigSaw and other cyberattacks, sign up for a free, personalized demo.
You will receive regular updates on the latest news on cybersecurity.
© 2021 Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.